1 本节介绍
📝本节您将学习如何通过庐山派来检测人脸朝向,如无特殊说明,以后所有例程的显示设备均为通过外接立创·3.1寸屏幕扩展板,在3.1寸小屏幕上显示。若用户无3.1寸屏幕扩展板也可以正常在IDE的缓冲区,只是受限于USB带宽,可能会帧率较低或卡顿。
🏆学习目标
1️⃣如何用庐山派开发板去检测人脸朝向。
2️⃣如何获取人脸朝向的欧拉角信息。
庐山派开发板的固件是存储在TF中的,模型文件已经提前写入到固件中了,所以大家只需要复制下面的代码到IDE,传递到开发板上就可以正常运行了。无需再额外拷贝,至于后面需要拷贝自己训练的模型那就是后话了。
在人脸朝向检测中,我们主要实现的就是通过摄像头捕获图像,检测人脸的位置,然后去计算人脸的姿态(俯仰角Pitch、偏航角Yaw、滚转角Roll)。这些信息可广泛应用于人机交互、驾驶员疲劳检测和增强现实等领域。和之前介绍的例程类似,他也是先通过人脸检测来定位图像中的人脸,然后在这个人脸范围内去计算人脸的旋转矩阵(3x3矩阵),并转化成欧拉角方便显示。
用这个代码再进行下一步应用层的编写,我们就能判断面向摄像头的人脸是否正视镜头、是否处于侧脸状态、是否低头或者仰头。
2 代码历程
from libs.PipeLine import PipeLine, ScopedTiming
from libs.AIBase import AIBase
from libs.AI2D import Ai2d
import os
import ujson
from media.media import *
from time import *
import nncase_runtime as nn
import ulab.numpy as np
import time
import image
import aidemo
import random
import gc
import sys
# 自定义人脸检测任务类
class FaceDetApp(AIBase):
def __init__(self,kmodel_path,model_input_size,anchors,confidence_threshold=0.25,nms_threshold=0.3,rgb888p_size=[1280,720],display_size=[1920,1080],debug_mode=0):
super().__init__(kmodel_path,model_input_size,rgb888p_size,debug_mode)
# kmodel路径
self.kmodel_path=kmodel_path
# 检测模型输入分辨率
self.model_input_size=model_input_size
# 置信度阈值
self.confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold
# nms阈值
self.nms_threshold=nms_threshold
self.anchors=anchors
# sensor给到AI的图像分辨率,宽16字节对齐
self.rgb888p_size=[ALIGN_UP(rgb888p_size[0],16),rgb888p_size[1]]
# 视频输出VO分辨率,宽16字节对齐
self.display_size=[ALIGN_UP(display_size[0],16),display_size[1]]
# debug模式
self.debug_mode=debug_mode
# 实例化Ai2d,用于实现模型预处理
self.ai2d=Ai2d(debug_mode)
# 设置Ai2d的输入输出格式和类型
self.ai2d.set_ai2d_dtype(nn.ai2d_format.NCHW_FMT,nn.ai2d_format.NCHW_FMT,np.uint8, np.uint8)
# 配置预处理操作,这里使用了pad和resize,Ai2d支持crop/shift/pad/resize/affine,具体代码请打开/sdcard/app/libs/AI2D.py查看
def config_preprocess(self,input_image_size=None):
with ScopedTiming("set preprocess config",self.debug_mode > 0):
# 初始化ai2d预处理配置,默认为sensor给到AI的尺寸,可以通过设置input_image_size自行修改输入尺寸
ai2d_input_size=input_image_size if input_image_size else self.rgb888p_size
# 计算padding参数,并设置padding预处理
self.ai2d.pad(self.get_pad_param(), 0, [104,117,123])
# 设置resize预处理
self.ai2d.resize(nn.interp_method.tf_bilinear, nn.interp_mode.half_pixel)
# 构建预处理流程,参数为预处理输入tensor的shape和预处理输出的tensor的shape
self.ai2d.build([1,3,ai2d_input_size[1],ai2d_input_size[0]],[1,3,self.model_input_size[1],self.model_input_size[0]])
# 自定义后处理,results是模型输出的array列表,这里使用了aidemo库的face_det_post_process接口
def postprocess(self,results):
with ScopedTiming("postprocess",self.debug_mode > 0):
res = aidemo.face_det_post_process(self.confidence_threshold,self.nms_threshold,self.model_input_size[0],self.anchors,self.rgb888p_size,results)
if len(res)==0:
return res
else:
return res[0]
# 计算padding参数
def get_pad_param(self):
dst_w = self.model_input_size[0]
dst_h = self.model_input_size[1]
# 计算最小的缩放比例,等比例缩放
ratio_w = dst_w / self.rgb888p_size[0]
ratio_h = dst_h / self.rgb888p_size[1]
if ratio_w < ratio_h:
ratio = ratio_w
else:
ratio = ratio_h
new_w = (int)(ratio * self.rgb888p_size[0])
new_h = (int)(ratio * self.rgb888p_size[1])
dw = (dst_w - new_w) / 2
dh = (dst_h - new_h) / 2
top = (int)(round(0))
bottom = (int)(round(dh * 2 + 0.1))
left = (int)(round(0))
right = (int)(round(dw * 2 - 0.1))
return [0,0,0,0,top, bottom, left, right]
# 自定义人脸姿态任务类
class FacePoseApp(AIBase):
def __init__(self,kmodel_path,model_input_size,rgb888p_size=[1920,1080],display_size=[1920,1080],debug_mode=0):
super().__init__(kmodel_path,model_input_size,rgb888p_size,debug_mode)
# kmodel路径
self.kmodel_path=kmodel_path
# 人脸姿态模型输入分辨率
self.model_input_size=model_input_size
# sensor给到AI的图像分辨率,宽16字节对齐
self.rgb888p_size=[ALIGN_UP(rgb888p_size[0],16),rgb888p_size[1]]
# 视频输出VO分辨率,宽16字节对齐
self.display_size=[ALIGN_UP(display_size[0],16),display_size[1]]
# debug模式
self.debug_mode=debug_mode
# 实例化Ai2d,用于实现模型预处理
self.ai2d=Ai2d(debug_mode)
# 设置Ai2d的输入输出格式和类型
self.ai2d.set_ai2d_dtype(nn.ai2d_format.NCHW_FMT,nn.ai2d_format.NCHW_FMT,np.uint8, np.uint8)
# 配置预处理操作,这里使用了affine,Ai2d支持crop/shift/pad/resize/affine,具体代码请打开/sdcard/app/libs/AI2D.py查看
def config_preprocess(self,det,input_image_size=None):
with ScopedTiming("set preprocess config",self.debug_mode > 0):
# 初始化ai2d预处理配置,默认为sensor给到AI的尺寸,可以通过设置input_image_size自行修改输入尺寸
ai2d_input_size=input_image_size if input_image_size else self.rgb888p_size
# 计算affine矩阵并设置affine预处理
matrix_dst = self.get_affine_matrix(det)
self.ai2d.affine(nn.interp_method.cv2_bilinear,0, 0, 127, 1,matrix_dst)
# 构建预处理流程,参数为预处理输入tensor的shape和预处理输出的tensor的shape
self.ai2d.build([1,3,ai2d_input_size[1],ai2d_input_size[0]],[1,3,self.model_input_size[1],self.model_input_size[0]])
# 自定义后处理,results是模型输出的array列表,计算欧拉角
def postprocess(self,results):
with ScopedTiming("postprocess",self.debug_mode > 0):
R,eular = self.get_euler(results[0][0])
return R,eular
def get_affine_matrix(self,bbox):
# 获取仿射矩阵,用于将边界框映射到模型输入空间
with ScopedTiming("get_affine_matrix", self.debug_mode > 1):
# 设置缩放因子
factor = 2.7
# 从边界框提取坐标和尺寸
x1, y1, w, h = map(lambda x: int(round(x, 0)), bbox[:4])
# 模型输入大小
edge_size = self.model_input_size[1]
# 平移距离,使得模型输入空间的中心对准原点
trans_distance = edge_size / 2.0
# 计算边界框中心点的坐标
center_x = x1 + w / 2.0
center_y = y1 + h / 2.0
# 计算最大边长
maximum_edge = factor * (h if h > w else w)
# 计算缩放比例
scale = edge_size * 2.0 / maximum_edge
# 计算平移参数
cx = trans_distance - scale * center_x
cy = trans_distance - scale * center_y
# 创建仿射矩阵
affine_matrix = [scale, 0, cx, 0, scale, cy]
return affine_matrix
def rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(self,R):
# 将旋转矩阵(3x3 矩阵)转换为欧拉角(pitch、yaw、roll)
# 计算 sin(yaw)
sy = np.sqrt(R[0, 0] ** 2 + R[1, 0] ** 2)
if sy < 1e-6:
# 若 sin(yaw) 过小,说明 pitch 接近 ±90 度
pitch = np.arctan2(-R[1, 2], R[1, 1]) * 180 / np.pi
yaw = np.arctan2(-R[2, 0], sy) * 180 / np.pi
roll = 0
else:
# 计算 pitch、yaw、roll 的角度
pitch = np.arctan2(R[2, 1], R[2, 2]) * 180 / np.pi
yaw = np.arctan2(-R[2, 0], sy) * 180 / np.pi
roll = np.arctan2(R[1, 0], R[0, 0]) * 180 / np.pi
return [pitch,yaw,roll]
def get_euler(self,data):
# 获取旋转矩阵和欧拉角
R = data[:3, :3].copy()
eular = self.rotation_matrix_to_euler_angles(R)
return R,eular
# 人脸姿态任务类
class FacePose:
def __init__(self,face_det_kmodel,face_pose_kmodel,det_input_size,pose_input_size,anchors,confidence_threshold=0.25,nms_threshold=0.3,rgb888p_size=[1280,720],display_size=[1920,1080],debug_mode=0):
# 人脸检测模型路径
self.face_det_kmodel=face_det_kmodel
# 人脸姿态模型路径
self.face_pose_kmodel=face_pose_kmodel
# 人脸检测模型输入分辨率
self.det_input_size=det_input_size
# 人脸姿态模型输入分辨率
self.pose_input_size=pose_input_size
# anchors
self.anchors=anchors
# 置信度阈值
self.confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold
# nms阈值
self.nms_threshold=nms_threshold
# sensor给到AI的图像分辨率,宽16字节对齐
self.rgb888p_size=[ALIGN_UP(rgb888p_size[0],16),rgb888p_size[1]]
# 视频输出VO分辨率,宽16字节对齐
self.display_size=[ALIGN_UP(display_size[0],16),display_size[1]]
# debug_mode模式
self.debug_mode=debug_mode
self.face_det=FaceDetApp(self.face_det_kmodel,model_input_size=self.det_input_size,anchors=self.anchors,confidence_threshold=self.confidence_threshold,nms_threshold=self.nms_threshold,rgb888p_size=self.rgb888p_size,display_size=self.display_size,debug_mode=0)
self.face_pose=FacePoseApp(self.face_pose_kmodel,model_input_size=self.pose_input_size,rgb888p_size=self.rgb888p_size,display_size=self.display_size)
self.face_det.config_preprocess()
# run函数
def run(self,input_np):
# 人脸检测
det_boxes=self.face_det.run(input_np)
pose_res=[]
for det_box in det_boxes:
# 对检测到的每一个人脸做人脸姿态估计
self.face_pose.config_preprocess(det_box)
R,eular=self.face_pose.run(input_np)
pose_res.append((R,eular))
return det_boxes,pose_res
# 绘制人脸姿态角效果
def draw_result(self,pl,dets,pose_res):
pl.osd_img.clear()
if dets:
draw_img_np = np.zeros((self.display_size[1],self.display_size[0],4),dtype=np.uint8)
draw_img=image.Image(self.display_size[0], self.display_size[1], image.ARGB8888,alloc=image.ALLOC_REF,data=draw_img_np)
line_color = np.array([255, 0, 0 ,255],dtype=np.uint8) #bgra
for i,det in enumerate(dets):
# (1)获取人脸姿态矩阵和欧拉角
projections,center_point = self.build_projection_matrix(det)
R,euler = pose_res[i]
# (2)遍历人脸投影矩阵的关键点,进行投影,并将结果画在图像上
first_points = []
second_points = []
for pp in range(8):
sum_x, sum_y = 0.0, 0.0
for cc in range(3):
sum_x += projections[pp][cc] * R[cc][0]
sum_y += projections[pp][cc] * (-R[cc][1])
center_x,center_y = center_point[0],center_point[1]
x = (sum_x + center_x) / self.rgb888p_size[0] * self.display_size[0]
y = (sum_y + center_y) / self.rgb888p_size[1] * self.display_size[1]
x = max(0, min(x, self.display_size[0]))
y = max(0, min(y, self.display_size[1]))
if pp < 4:
first_points.append((x, y))
else:
second_points.append((x, y))
first_points = np.array(first_points,dtype=np.float)
aidemo.polylines(draw_img_np,first_points,True,line_color,2,8,0)
second_points = np.array(second_points,dtype=np.float)
aidemo.polylines(draw_img_np,second_points,True,line_color,2,8,0)
for ll in range(4):
x0, y0 = int(first_points[ll][0]),int(first_points[ll][1])
x1, y1 = int(second_points[ll][0]),int(second_points[ll][1])
draw_img.draw_line(x0, y0, x1, y1, color = (255, 0, 0 ,255), thickness = 2)
pl.osd_img.copy_from(draw_img)
def build_projection_matrix(self,det):
x1, y1, w, h = map(lambda x: int(round(x, 0)), det[:4])
# 计算边界框中心坐标
center_x = x1 + w / 2.0
center_y = y1 + h / 2.0
# 定义后部(rear)和前部(front)的尺寸和深度
rear_width = 0.5 * w
rear_height = 0.5 * h
rear_depth = 0
factor = np.sqrt(2.0)
front_width = factor * rear_width
front_height = factor * rear_height
front_depth = factor * rear_width # 使用宽度来计算深度,也可以使用高度,取决于需求
# 定义立方体的顶点坐标
temp = [
[-rear_width, -rear_height, rear_depth],
[-rear_width, rear_height, rear_depth],
[rear_width, rear_height, rear_depth],
[rear_width, -rear_height, rear_depth],
[-front_width, -front_height, front_depth],
[-front_width, front_height, front_depth],
[front_width, front_height, front_depth],
[front_width, -front_height, front_depth]
]
projections = np.array(temp)
# 返回投影矩阵和中心坐标
return projections, (center_x, center_y)
if __name__=="__main__":
# 显示模式,默认"hdmi",可以选择"hdmi"和"lcd"
display_mode="lcd"
# k230保持不变,k230d可调整为[640,360]
rgb888p_size = [1920, 1080]
if display_mode=="hdmi":
display_size=[1920,1080]
else:
display_size=[800,480]
# 人脸检测模型路径
face_det_kmodel_path="/sdcard/examples/kmodel/face_detection_320.kmodel"
# 人脸姿态模型路径
face_pose_kmodel_path="/sdcard/examples/kmodel/face_pose.kmodel"
# 其它参数
anchors_path="/sdcard/examples/utils/prior_data_320.bin"
face_det_input_size=[320,320]
face_pose_input_size=[120,120]
confidence_threshold=0.5
nms_threshold=0.2
anchor_len=4200
det_dim=4
anchors = np.fromfile(anchors_path, dtype=np.float)
anchors = anchors.reshape((anchor_len,det_dim))
# 初始化PipeLine,只关注传给AI的图像分辨率,显示的分辨率
pl=PipeLine(rgb888p_size=rgb888p_size,display_size=display_size,display_mode=display_mode)
pl.create()
fp=FacePose(face_det_kmodel_path,face_pose_kmodel_path,det_input_size=face_det_input_size,pose_input_size=face_pose_input_size,anchors=anchors,confidence_threshold=confidence_threshold,nms_threshold=nms_threshold,rgb888p_size=rgb888p_size,display_size=display_size)
try:
while True:
os.exitpoint()
with ScopedTiming("total",1):
img=pl.get_frame() # 获取当前帧
det_boxes,pose_res=fp.run(img) # 推理当前帧
fp.draw_result(pl,det_boxes,pose_res) # 绘制推理效果
pl.show_image() # 展示推理效果
gc.collect()
except Exception as e:
sys.print_exception(e)
finally:
fp.face_det.deinit()
fp.face_pose.deinit()
pl.destroy()2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
人脸检测(FaceDetApp类):用于加载人脸检测模型,利用AI2d对原始图像进行处理,然后输出人脸框的坐标和尺寸。
人脸姿态估计(FacePoseApp类):从上一步中获取基于人脸检测得到的人脸框,进行裁剪和变换,用姿态模型来推理出旋转矩阵,再用这个旋转矩阵算出欧拉角。最后就进行示意框架的绘制就好了
得到的欧拉角可以描述人脸在三维空间的转动情况:
- pitch(俯仰角):头部上下抬头、低头角度
- yaw(偏航角):头部左右转动角度
- roll(翻滚角):头部左右倾斜角度
3 运行效果
首先我们准备几张人脸不同朝向的图片: 
在IDE中的运行效果如下所示: 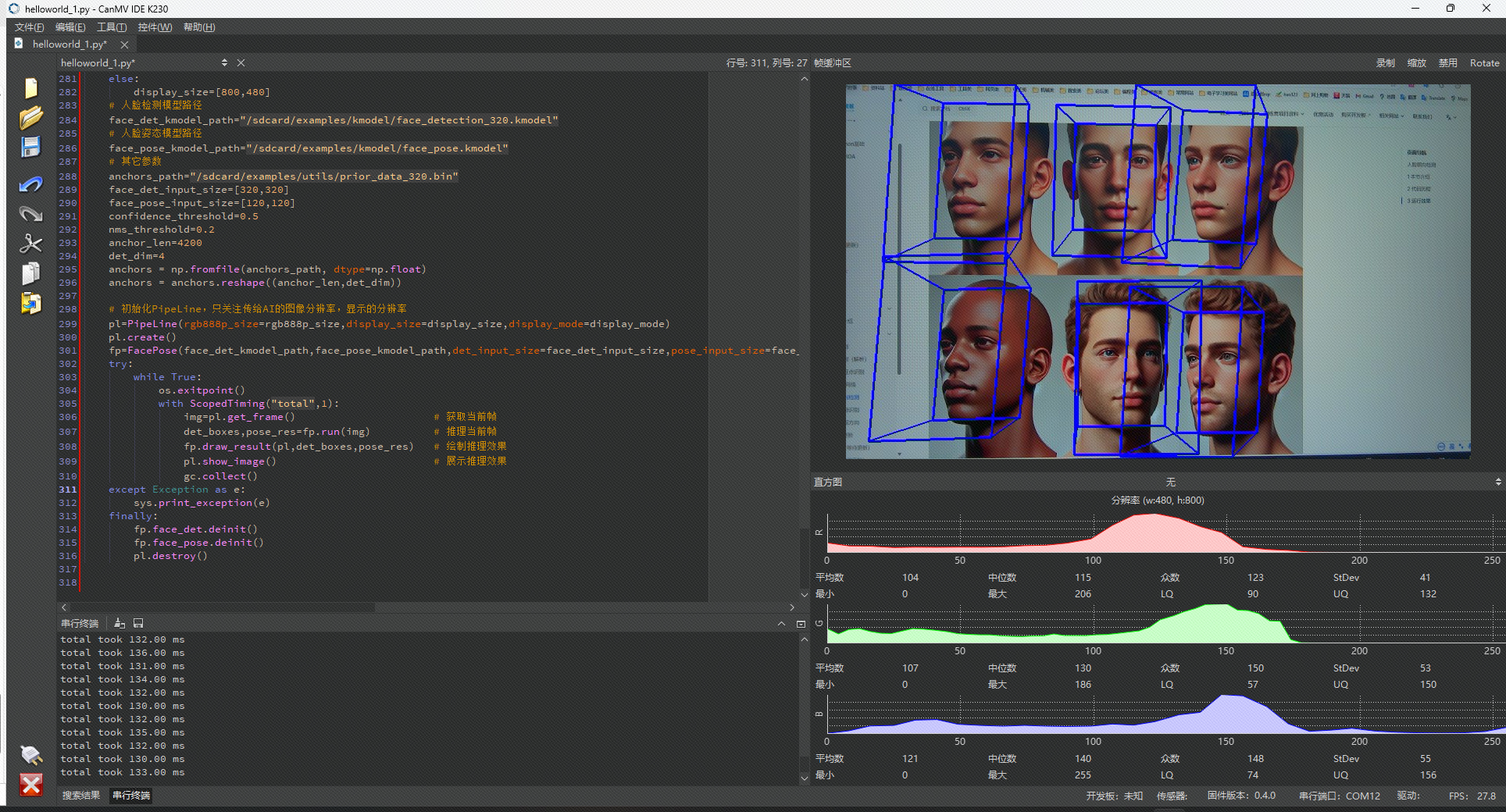
4 获取人脸朝向信息
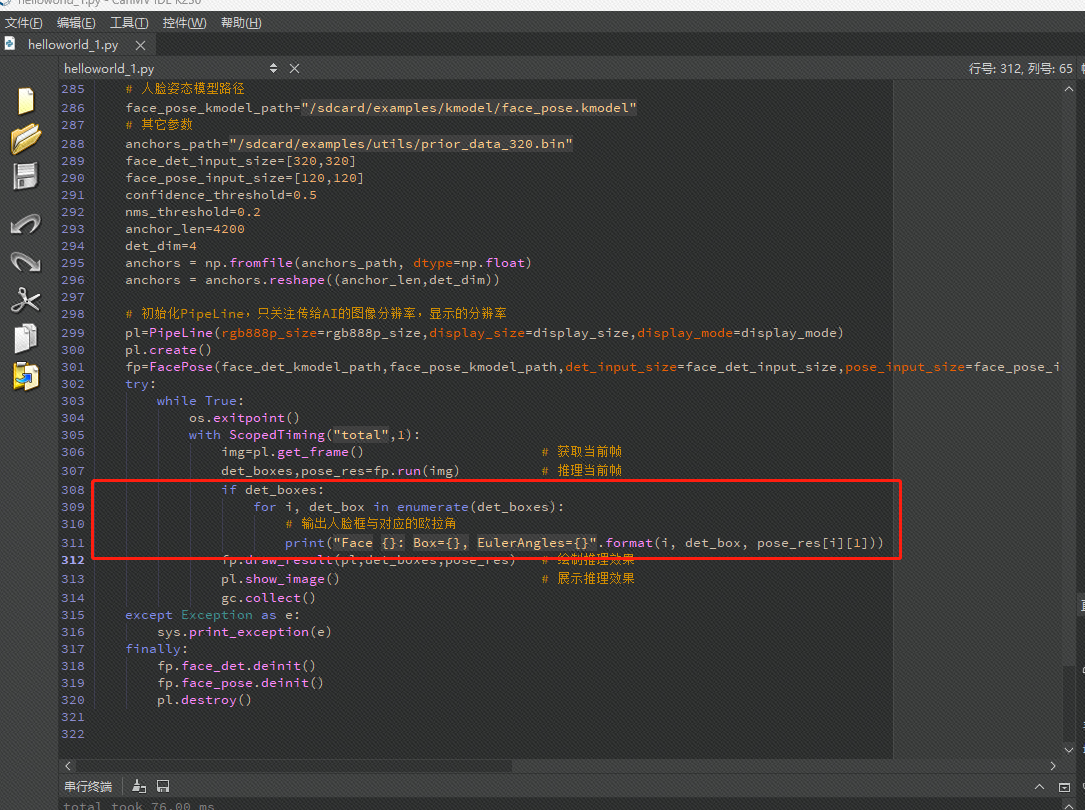
在主函数的推理结束帧 det_boxes,pose_res=fp.run(img) # 推理当前帧结束后加入以下内容:
if det_boxes:
for i, det_box in enumerate(det_boxes):
# 输出人脸框与对应的欧拉角
print("Face {}: Box={}, EulerAngles={}".format(i, det_box, pose_res[i][1]))2
3
4
添加位置如下图所示:
继续将摄像头对准这些不同朝向的人脸,我们可以看到IDE的串行终端就会打印人脸的朝向信息了:
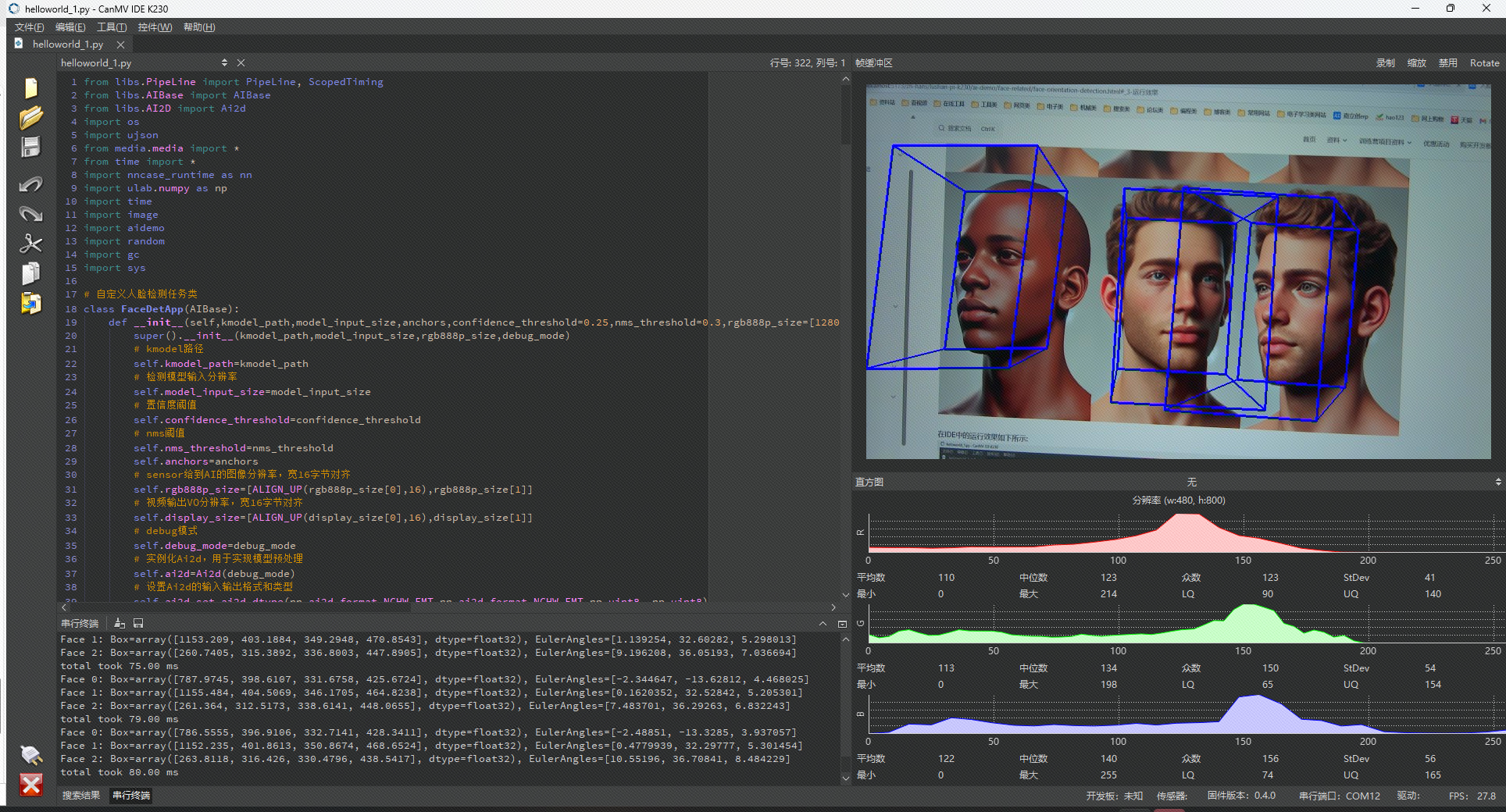
我这里是检测到了三个人脸:
Face 0: Box=array([787.6563, 377.3204, 320.6874, 421.6591], dtype=float32), EulerAngles=[-2.656312, -13.3022, 4.123715]
Face 1: Box=array([1141.927, 406.385, 336.9648, 443.1049], dtype=float32), EulerAngles=[0.9286932, 31.24547, 6.115503]
Face 2: Box=array([269.4192, 307.4334, 315.1303, 441.2481], dtype=float32), EulerAngles=[8.293209, 36.21836, 6.351421]
total took 76.00 ms2
3
4
首先,Face 0, Face 1, Face 2表示检测到的第0张、第1张和第2张人脸,每个编号对应一张人脸。后面跟的Box表示人脸框的位置和大小,用一个数组来表示:[x, y, width, height],x 和 y 是人脸框左上角的坐标,width 是人脸框的宽度,height 是人脸框的高度。
从坐标信息中我们可以看到(靠X坐标来判断),Face0是中间的脸,Face1是右边的脸,Face2是最左边的脸。
然后EulerAngles表示姿态估计的结果,用三个欧拉角来描述人脸在三维空间的旋转情况:
Pitch(俯仰角):脸是往上抬还是往下低,例如 Face 0 的 -2.656312 表示略微低头。
Yaw(偏航角):脸是往左转还是往右转,例如 Face 0 的 -13.3022 表示偏向左边。
Roll(翻滚角):脸是往左倾斜还是往右倾斜,例如 Face 0 的 4.123715 表示略向右倾斜。
最后的total took 76ms就表示我们的庐山派开发板在整个预处理,检测,姿态推到后处理总共花了76毫秒,意思就是处理单张静态图花了这么长的时间。
如果需要将这些信息传递给外部设备,我们就可以结合之前我们学过的UART章节,将这些信息传递给外部设备了。