04、SPI device设备树处理过程

参考资料:
- 内核头文件:
include\linux\spi\spi.h - 内核文档:
Documentation\devicetree\bindings\spi\spi-bus.txt - 内核源码:
drivers\spi\spi.c
一、spi_device结构体
struct spi_device {
struct device dev;
struct spi_controller *controller;
struct spi_controller *master; /* compatibility layer */
u32 max_speed_hz;
u8 chip_select;
u8 bits_per_word;
bool rt;
u32 mode;
#define SPI_CPHA 0x01 /* clock phase */
#define SPI_CPOL 0x02 /* clock polarity */
#define SPI_MODE_0 (0|0) /* (original MicroWire) */
#define SPI_MODE_1 (0|SPI_CPHA)
#define SPI_MODE_2 (SPI_CPOL|0)
#define SPI_MODE_3 (SPI_CPOL|SPI_CPHA)
#define SPI_CS_HIGH 0x04 /* chipselect active high? */
#define SPI_LSB_FIRST 0x08 /* per-word bits-on-wire */
#define SPI_3WIRE 0x10 /* SI/SO signals shared */
#define SPI_LOOP 0x20 /* loopback mode */
#define SPI_NO_CS 0x40 /* 1 dev/bus, no chipselect */
#define SPI_READY 0x80 /* slave pulls low to pause */
#define SPI_TX_DUAL 0x100 /* transmit with 2 wires */
#define SPI_TX_QUAD 0x200 /* transmit with 4 wires */
#define SPI_RX_DUAL 0x400 /* receive with 2 wires */
#define SPI_RX_QUAD 0x800 /* receive with 4 wires */
#define SPI_CS_WORD 0x1000 /* toggle cs after each word */
#define SPI_TX_OCTAL 0x2000 /* transmit with 8 wires */
#define SPI_RX_OCTAL 0x4000 /* receive with 8 wires */
#define SPI_3WIRE_HIZ 0x8000 /* high impedance turnaround */
int irq;
void *controller_state;
void *controller_data;
char modalias[SPI_NAME_SIZE];
const char *driver_override;
int cs_gpio; /* LEGACY: chip select gpio */
struct gpio_desc *cs_gpiod; /* chip select gpio desc */
struct spi_delay word_delay; /* inter-word delay */
/* the statistics */
struct spi_statistics statistics;
/*
* likely need more hooks for more protocol options affecting how
* the controller talks to each chip, like:
* - memory packing (12 bit samples into low bits, others zeroed)
* - priority
* - chipselect delays
* - ...
*/
};2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
各个成员含义如下:
max_speed_hz:该设备能支持的SPI时钟最大值
chip_select:是这个spi_master下的第几个设备
- 在spi_master中有一个cs_gpios数组,里面存放有下面各个spi设备的片选引脚
- spi_device的片选引脚就是:cs_gpios[spi_device.chip_select]
cs_gpio:这是可选项,也可以把spi_device的片选引脚记录在这里
bits_per_word:每个基本的SPI传输涉及多少位
- word:我们使用SPI控制器时,一般是往某个寄存器里写入数据,SPI控制器就会把这些数据一位一位地发送出去
- 一个寄存器是32位的,被称为一个word(有时候也称为double word)
- 这个寄存器里多少位会被发送出去?使用bits_per_word来表示
- 扩展:bits_per_word是可以大于32的,也就是每次SPI传输可能会发送多于32位的数据,这适用于DMA突发传输
mode:含义广泛,看看结构体里那些宏
SPI_CPHA:在第1个周期采样,在第2个周期采样?
SPI_CPOL:平时时钟极性
- SPI_CPHA和SPI_CPOL组合起来就可以得到4种模式
- SPI_MODE_0:平时SCK为低(SPI_CPOL为0),在第1个周期采样(SPI_CPHA为0)
- SPI_MODE_1:平时SCK为低(SPI_CPOL为0),在第2个周期采样(SPI_CPHA为1)
- SPI_MODE_2:平时SCK为高(SPI_CPOL为1),在第1个周期采样(SPI_CPHA为0)
- SPI_MODE_3:平时SCK为高(SPI_CPOL为1),在第2个周期采样(SPI_CPHA为1)
SPI_CS_HIGH:一般来说片选引脚时低电平有效,SPI_CS_HIGH表示高电平有效
SPI_LSB_FIRST:
- 一般来说先传输MSB(最高位),SPI_LSB_FIRST表示先传LSB(最低位);
- 很多SPI控制器并不支持SPI_LSB_FIRST
SPI_3WIRE:SO、SI共用一条线
SPI_LOOP:回环模式,就是SO、SI连接在一起
SPI_NO_CS:只有一个SPI设备,没有片选信号,也不需要片选信号
SPI_READY:SPI从设备可以拉低信号,表示暂停、表示未就绪
SPI_TX_DUAL:发送数据时有2条信号线
SPI_TX_QUAD:发送数据时有4条信号线
SPI_RX_DUAL:接收数据时有2条信号线
SPI_RX_QUAD:接收数据时有4条信号线
二、在开发板配置文件中实例化SPI设备(不推荐)
没有使用设备树,来对spi_devices(spi_register_board_info)
只有在系统不支持设备树的情况下,才应该在开发板文件中实例化设备。由于设备树已经出现,这种实例化方法已被弃用。因此,只要记住开发板文件驻留在arch/目录下即可。用于表示SPI设备的结构是struct spi_board_info,而不是驱动程序中使用的struct spi_device。只有当使用spi_register_board_info函数填充并注册struct spi_board_info时,内核才会构建struct spi_device(会将它传递给驱动程序,并向SPI内核注册)。
请查看include/linux/spi/spi.h中struct spi_board_info的各字段,spi_register_board_info定义在drivers/spi/spi.c中。现在来看一看某个SPI设备在开发板文件中的注册:
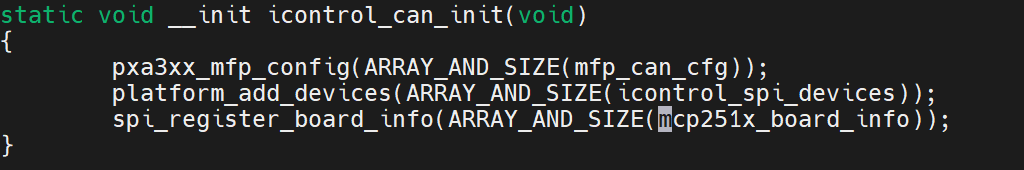
arm/mach-pxa/icontrol.c
static struct spi_board_info mcp251x_board_info[] = {
{
.modalias = "mcp2515",
.max_speed_hz = 6500000,
.bus_num = 3,
.chip_select = 0,
.platform_data = &mcp251x_info,
.controller_data = &mcp251x_chip_info1,
.irq = PXA_GPIO_TO_IRQ(ICONTROL_MCP251x_nIRQ1)
},
{
.modalias = "mcp2515",
.max_speed_hz = 6500000,
.bus_num = 3,
.chip_select = 1,
.platform_data = &mcp251x_info,
.controller_data = &mcp251x_chip_info2,
.irq = PXA_GPIO_TO_IRQ(ICONTROL_MCP251x_nIRQ2)
},
{
.modalias = "mcp2515",
.max_speed_hz = 6500000,
.bus_num = 4,
.chip_select = 0,
.platform_data = &mcp251x_info,
.controller_data = &mcp251x_chip_info3,
.irq = PXA_GPIO_TO_IRQ(ICONTROL_MCP251x_nIRQ3)
},
{
.modalias = "mcp2515",
.max_speed_hz = 6500000,
.bus_num = 4,
.chip_select = 1,
.platform_data = &mcp251x_info,
.controller_data = &mcp251x_chip_info4,
.irq = PXA_GPIO_TO_IRQ(ICONTROL_MCP251x_nIRQ4)
}
};2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
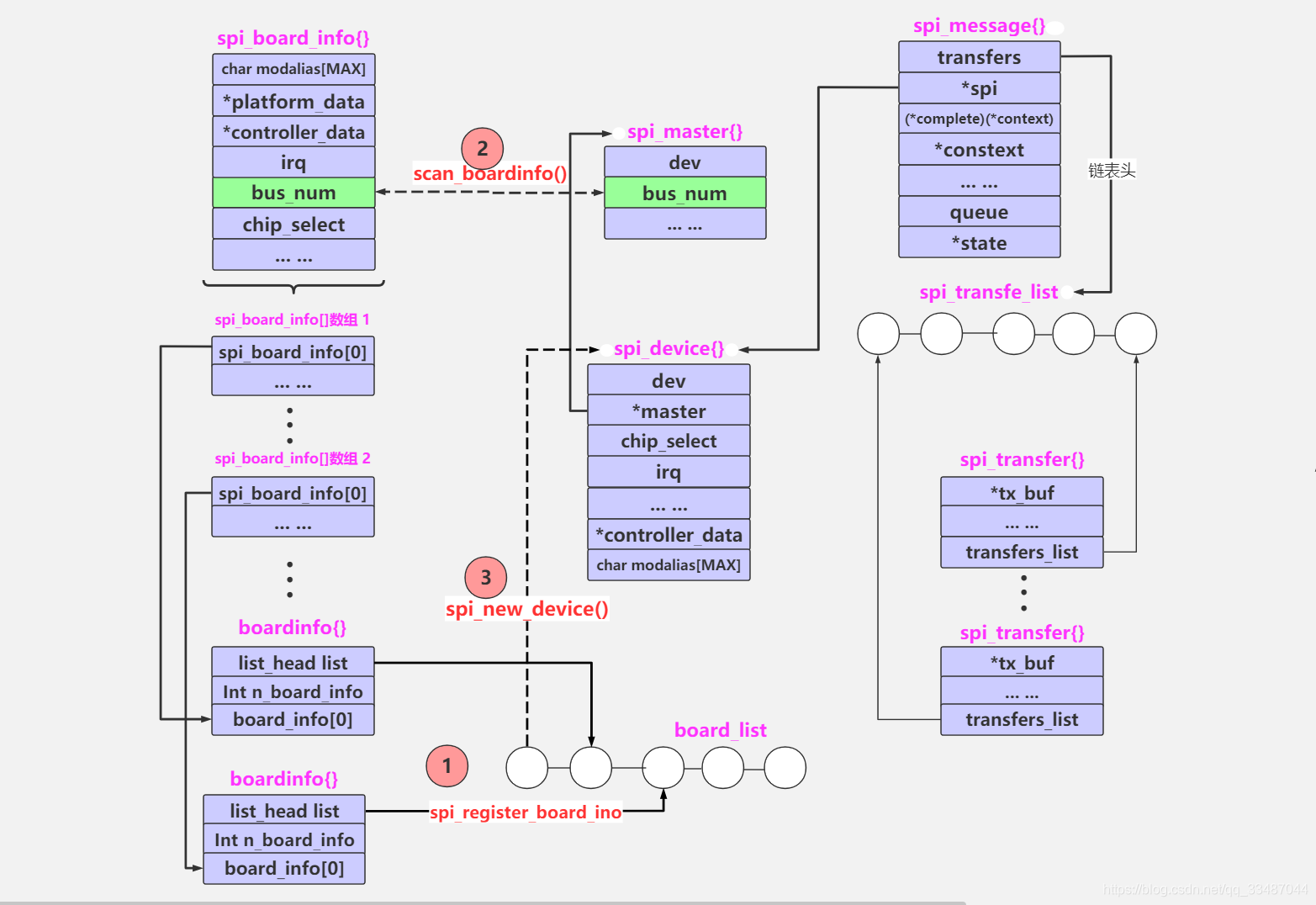
spi_register_board_info
int spi_register_board_info(struct spi_board_info const *info, unsigned n)
{
struct boardinfo *bi;
int i;
if (!n)
return 0;
bi = kcalloc(n, sizeof(*bi), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!bi)
return -ENOMEM;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++, bi++, info++) {
struct spi_controller *ctlr;
memcpy(&bi->board_info, info, sizeof(*info));
if (info->properties) {
bi->board_info.properties =
property_entries_dup(info->properties);
if (IS_ERR(bi->board_info.properties))
return PTR_ERR(bi->board_info.properties);
}
mutex_lock(&board_lock);
list_add_tail(&bi->list, &board_list);
list_for_each_entry(ctlr, &spi_controller_list, list)
spi_match_controller_to_boardinfo(ctlr,
&bi->board_info);
mutex_unlock(&board_lock);
}
return 0;
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
static void spi_match_controller_to_boardinfo(struct spi_controller *ctlr,
struct spi_board_info *bi)
{
struct spi_device *dev;
if (ctlr->bus_num != bi->bus_num)
return;
dev = spi_new_device(ctlr, bi);
if (!dev)
dev_err(ctlr->dev.parent, "can't create new device for %s\n",
bi->modalias);
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
三、SPI和设备树
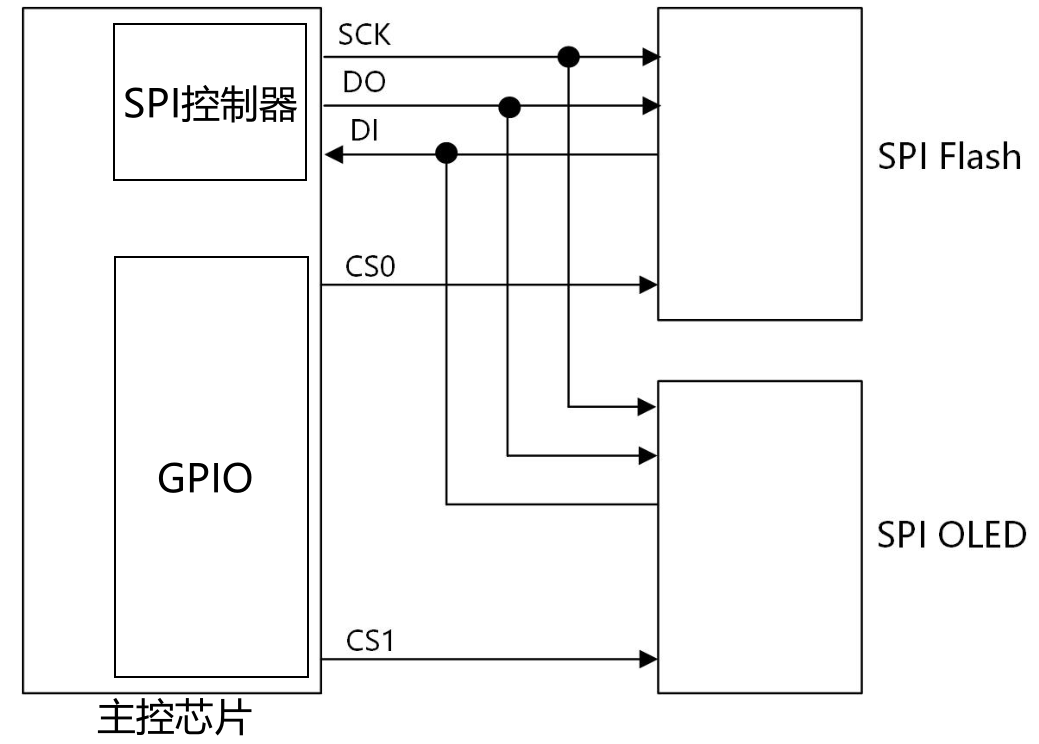
与I2C设备类似,SPI设备属于DT中的非存储器映射设备系列,但也可寻址。这里,地址是指分配给控制器(主设备)的CS列表的CS索引(从0开始)。举例来说,可能有3个不同的SPI设备位于SPI总线上,每个SPI设备都有其CS线路。主设备将得到一组GPIO,每个GPIO代表CS要激活设备。如果设备X使用第二条GPIO线作为CS,则必须在reg属性中将其地址设置为1(因为始终从0开始编号)。
3.1、SPI设备树格式
3.2、SPI Master
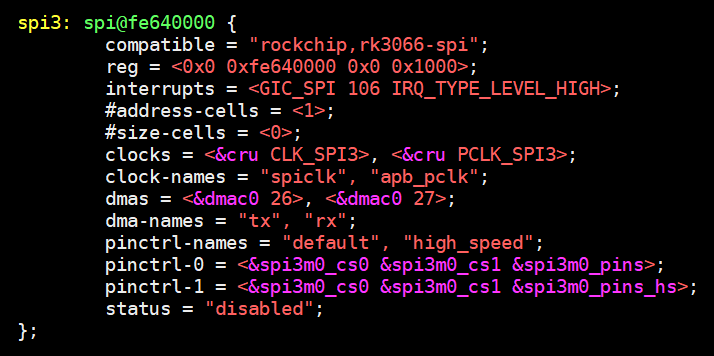
在设备树中,对于SPI Master,必须的属性如下:
- #address-cells:这个SPI Master下的SPI设备,需要多少个cell来表述它的片选引脚
- #size-cells:必须设置为0
- compatible:根据它找到SPI Master驱动
可选的属性如下:
- cs-gpios:SPI Master可以使用多个GPIO当做片选,可以在这个属性列出那些GPIO
- num-cs:片选引脚总数
其他属性都是驱动程序相关的,不同的SPI Master驱动程序要求的属性可能不一样。
3.3、SPI Device
在SPI Master对应的设备树节点下,每一个子节点都对应一个SPI设备,这个SPI设备连接在该SPI Master下面。
这些子节点中,必选的属性如下:
- compatible:根据它找到SPI Device驱动
- reg:用来表示它使用哪个片选引脚
- spi-max-frequency:必选,该SPI设备支持的最大SPI时钟
可选的属性如下:
- spi-cpol:这是一个空属性(没有值),表示CPOL为1,即平时SPI时钟为低电平
- spi-cpha:这是一个空属性(没有值),表示CPHA为1),即在时钟的第2个边沿采样数据
- spi-cs-high:这是一个空属性(没有值),表示片选引脚高电平有效
- spi-3wire:这是一个空属性(没有值),表示使用SPI 三线模式
- spi-lsb-first:这是一个空属性(没有值),表示使用SPI传输数据时先传输最低位(LSB)
- spi-tx-bus-width:表示有几条MOSI引脚;没有这个属性时默认只有1条MOSI引脚
- spi-rx-bus-width:表示有几条MISO引脚;没有这个属性时默认只有1条MISO引脚
- spi-rx-delay-us:单位是毫秒,表示每次
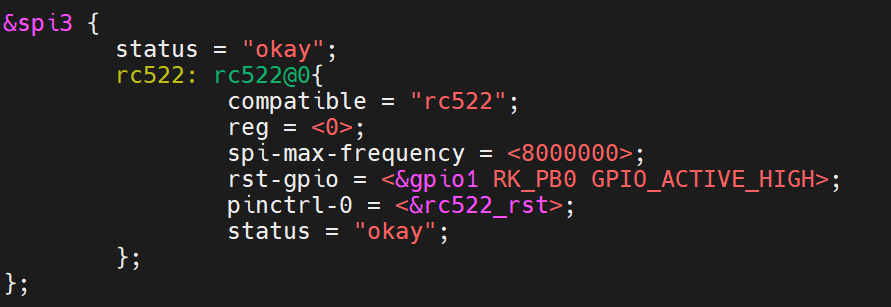
tspi-rk3566-user-v10.dts
3.4、设备树处理过程
int spi_register_controller(struct spi_controller *ctlr)----->of_register_spi_devices
static struct spi_device *
of_register_spi_device(struct spi_controller *ctlr, struct device_node *nc)
{
struct spi_device *spi;
int rc;
/* Alloc an spi_device */
spi = spi_alloc_device(ctlr);
if (!spi) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "spi_device alloc error for %pOF\n", nc);
rc = -ENOMEM;
goto err_out;
}
/* Select device driver */
rc = of_modalias_node(nc, spi->modalias,
sizeof(spi->modalias));
if (rc < 0) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "cannot find modalias for %pOF\n", nc);
goto err_out;
}
rc = of_spi_parse_dt(ctlr, spi, nc);
if (rc)
goto err_out;
/* Store a pointer to the node in the device structure */
of_node_get(nc);
spi->dev.of_node = nc;
spi->dev.fwnode = of_fwnode_handle(nc);
/* Register the new device */
rc = spi_add_device(spi);
if (rc) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "spi_device register error %pOF\n", nc);
goto err_of_node_put;
}
return spi;
err_of_node_put:
of_node_put(nc);
err_out:
spi_dev_put(spi);
return ERR_PTR(rc);
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
①spi_alloc_device
struct spi_device *spi_alloc_device(struct spi_controller *ctlr)
{
struct spi_device *spi;
if (!spi_controller_get(ctlr))
return NULL;
spi = kzalloc(sizeof(*spi), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!spi) {
spi_controller_put(ctlr);
return NULL;
}
spi->master = spi->controller = ctlr;
spi->dev.parent = &ctlr->dev;
spi->dev.bus = &spi_bus_type;
spi->dev.release = spidev_release;
spi->cs_gpio = -ENOENT;
spin_lock_init(&spi->statistics.lock);
device_initialize(&spi->dev);
return spi;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_alloc_device);2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
② of_modalias_node
of/base.c
int of_modalias_node(struct device_node *node, char *modalias, int len)
{
const char *compatible, *p;
int cplen;
compatible = of_get_property(node, "compatible", &cplen);
if (!compatible || strlen(compatible) > cplen)
return -ENODEV;
p = strchr(compatible, ',');
strlcpy(modalias, p ? p + 1 : compatible, len);
return 0;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(of_modalias_node);2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
③ of_spi_parse_dt
static int of_spi_parse_dt(struct spi_controller *ctlr, struct spi_device *spi,
struct device_node *nc)
{
u32 value;
int rc;
/* Mode (clock phase/polarity/etc.) */
if (of_property_read_bool(nc, "spi-cpha"))
spi->mode |= SPI_CPHA;
if (of_property_read_bool(nc, "spi-cpol"))
spi->mode |= SPI_CPOL;
if (of_property_read_bool(nc, "spi-cs-high"))
spi->mode |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
if (of_property_read_bool(nc, "spi-3wire"))
spi->mode |= SPI_3WIRE;
if (of_property_read_bool(nc, "spi-lsb-first"))
spi->mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
/* Device DUAL/QUAD mode */
if (!of_property_read_u32(nc, "spi-tx-bus-width", &value)) {
switch (value) {
case 1:
break;
case 2:
spi->mode |= SPI_TX_DUAL;
break;
case 4:
spi->mode |= SPI_TX_QUAD;
break;
default:
dev_warn(&ctlr->dev,
"spi-tx-bus-width %d not supported\n",
value);
break;
}
}
if (!of_property_read_u32(nc, "spi-rx-bus-width", &value)) {
switch (value) {
case 1:
break;
case 2:
spi->mode |= SPI_RX_DUAL;
break;
case 4:
spi->mode |= SPI_RX_QUAD;
break;
default:
dev_warn(&ctlr->dev,
"spi-rx-bus-width %d not supported\n",
value);
break;
}
}
if (spi_controller_is_slave(ctlr)) {
if (strcmp(nc->name, "slave")) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "%pOF is not called 'slave'\n",
nc);
return -EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
/* Device address */
rc = of_property_read_u32(nc, "reg", &value);
if (rc) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev, "%pOF has no valid 'reg' property (%d)\n",
nc, rc);
return rc;
}
spi->chip_select = value;
/* Device speed */
rc = of_property_read_u32(nc, "spi-max-frequency", &value);
if (rc) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev,
"%pOF has no valid 'spi-max-frequency' property (%d)\n", nc, rc);
return rc;
}
spi->max_speed_hz = value;
return 0;
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
④ spi_add_device
spi/spi.c
/**
* spi_add_device - Add spi_device allocated with spi_alloc_device
* @spi: spi_device to register
*
* Companion function to spi_alloc_device. Devices allocated with
* spi_alloc_device can be added onto the spi bus with this function.
*
* Return: 0 on success; negative errno on failure
*/
int spi_add_device(struct spi_device *spi)
{
struct spi_controller *ctlr = spi->controller;
struct device *dev = ctlr->dev.parent;
int status;
/* Chipselects are numbered 0..max; validate. */
if (spi->chip_select >= ctlr->num_chipselect) {
dev_err(dev, "cs%d >= max %d\n", spi->chip_select,
ctlr->num_chipselect);
return -EINVAL;
}
/* Set the bus ID string */
spi_dev_set_name(spi);
/* We need to make sure there's no other device with this
* chipselect **BEFORE** we call setup(), else we'll trash
* its configuration. Lock against concurrent add() calls.
*/
mutex_lock(&spi_add_lock);
status = bus_for_each_dev(&spi_bus_type, NULL, spi, spi_dev_check);
if (status) {
dev_err(dev, "chipselect %d already in use\n",
spi->chip_select);
goto done;
}
/* Controller may unregister concurrently */
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SPI_DYNAMIC) &&
!device_is_registered(&ctlr->dev)) {
status = -ENODEV;
goto done;
}
if (ctlr->cs_gpios)
spi->cs_gpio = ctlr->cs_gpios[spi->chip_select];
/* Drivers may modify this initial i/o setup, but will
* normally rely on the device being setup. Devices
* using SPI_CS_HIGH can't coexist well otherwise...
*/
status = spi_setup(spi);
if (status < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "can't setup %s, status %d\n",
dev_name(&spi->dev), status);
goto done;
}
/* Device may be bound to an active driver when this returns */
status = device_add(&spi->dev);
if (status < 0)
dev_err(dev, "can't add %s, status %d\n",
dev_name(&spi->dev), status);
else
dev_dbg(dev, "registered child %s\n", dev_name(&spi->dev));
done:
mutex_unlock(&spi_add_lock);
return status;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(spi_add_device);2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
- spi_new_device
spi_new_device是函数spi_alloc_device和spi_add_device的结合,使用从实用性来说,最好不好单独调用spi_alloc_device和spi_add_device,而是调用这个 spi_new_device。
/**
* spi_new_device - instantiate one new SPI device
* @ctlr: Controller to which device is connected
* @chip: Describes the SPI device
* Context: can sleep
*
* On typical mainboards, this is purely internal; and it's not needed
* after board init creates the hard-wired devices. Some development
* platforms may not be able to use spi_register_board_info though, and
* this is exported so that for example a USB or parport based adapter
* driver could add devices (which it would learn about out-of-band).
*
* Return: the new device, or NULL.
*/
struct spi_device *spi_new_device(struct spi_controller *ctlr,
struct spi_board_info *chip)
{
struct spi_device *proxy;
int status;
/* NOTE: caller did any chip->bus_num checks necessary.
*
* Also, unless we change the return value convention to use
* error-or-pointer (not NULL-or-pointer), troubleshootability
* suggests syslogged diagnostics are best here (ugh).
*/
proxy = spi_alloc_device(ctlr);
if (!proxy)
return NULL;
WARN_ON(strlen(chip->modalias) >= sizeof(proxy->modalias));
proxy->chip_select = chip->chip_select;
proxy->max_speed_hz = chip->max_speed_hz;
proxy->mode = chip->mode;
proxy->irq = chip->irq;
strlcpy(proxy->modalias, chip->modalias, sizeof(proxy->modalias));
proxy->dev.platform_data = (void *) chip->platform_data;
proxy->controller_data = chip->controller_data;
proxy->controller_state = NULL;
if (chip->properties) {
status = device_add_properties(&proxy->dev, chip->properties);
if (status) {
dev_err(&ctlr->dev,
"failed to add properties to '%s': %d\n",
chip->modalias, status);
goto err_dev_put;
}
}
status = spi_add_device(proxy);
if (status < 0)
goto err_remove_props;
return proxy;
err_remove_props:
if (chip->properties)
device_remove_properties(&proxy->dev);
err_dev_put:
spi_dev_put(proxy);
return NULL;
}2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65