06、PHY工作的代码流程
一、初始化mdio子系统
mdio子系统继承了linux设备驱动模型,在mdio子系统初始化的过程中向内核设备驱动模型注册了mdio总线,mdio总线用来关联mdio设备和驱动。
mdio子系统的初始化在内核源码drivers/net/phy/phy_device.c中。
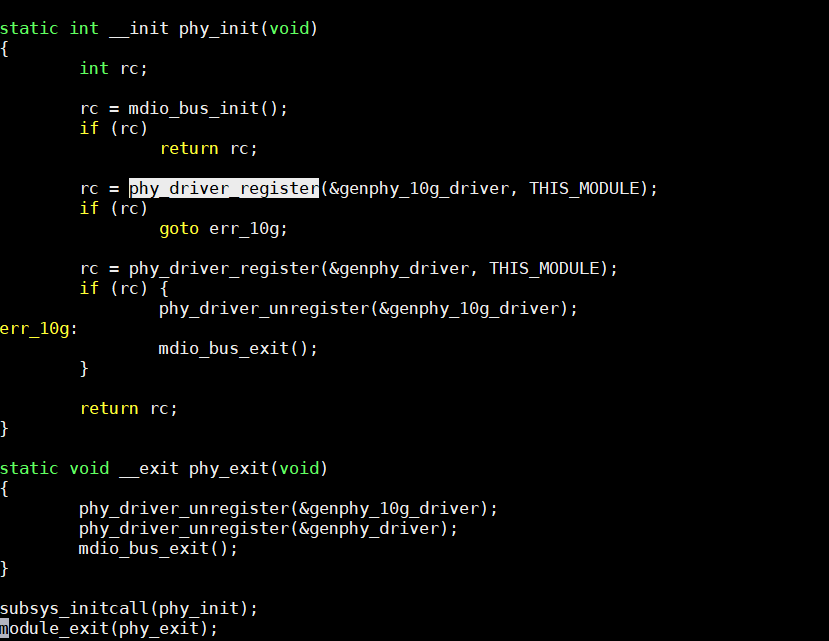
mdio_bus_init:
二、注册phy driver
在mdio子系统初始化的时候通过phy_driver_register接口注册了两个通用的phy驱动。其他phy驱动可以通过module_phy_driver宏注册到mdio子系统核心,以dp83848phy驱动为例,其注册代码如下:
module_phy_driver(realtek_drvs);module_phy_driver宏实现如下:
linux/phy.h
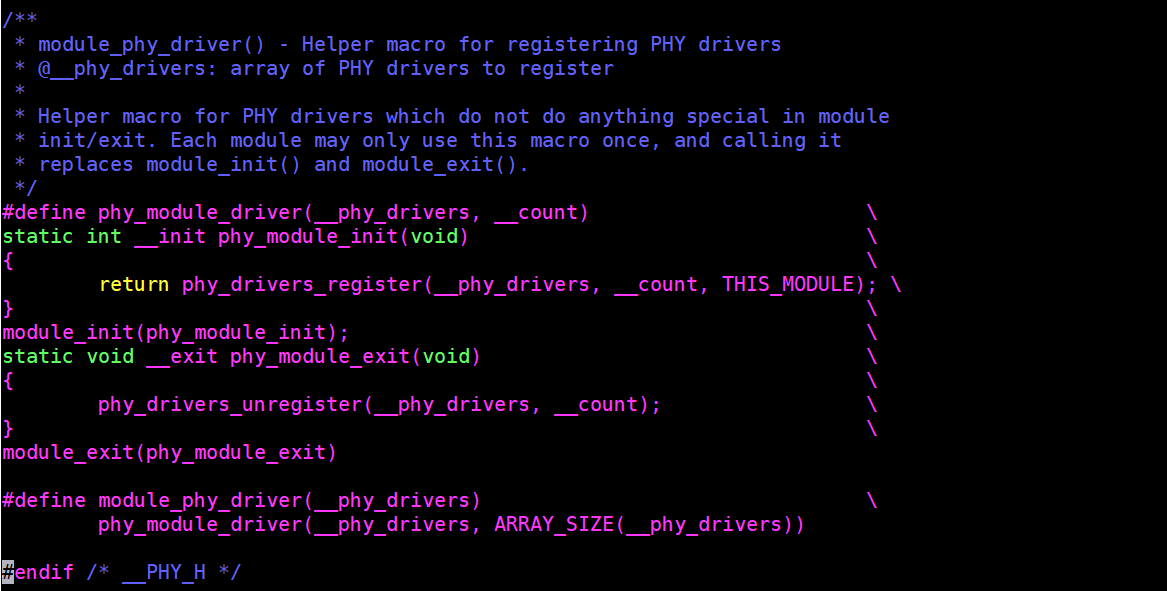
由上面的宏结构可知,其原理是通过module_init定义一个模块初始化函数,在模块初始化函数中调用phy_drivers_register接口注册phy_driver对象。
phy_drivers_register:
三、申请注册mii_bus
一般在网卡驱动的probe初始化网卡驱动的时候申请mii_bus,以stmmac网卡驱动为例,在其probe函数中调用stmmac_mdio_register()函数来初始化mii_bus,在该函数中申请了mii_bus并设置了read和write回调函数。
net/ethernet/stmicro/stmmac/stmmac_mdio.c
int stmmac_mdio_register(struct net_device *ndev)
{
int err = 0;
struct mii_bus *new_bus;
struct stmmac_priv *priv = netdev_priv(ndev);
struct stmmac_mdio_bus_data *mdio_bus_data = priv->plat->mdio_bus_data;
struct device_node *mdio_node = priv->plat->mdio_node;
struct device *dev = ndev->dev.parent;
int addr, found, max_addr;
if (!mdio_bus_data)
return 0;
new_bus = mdiobus_alloc();
if (!new_bus)
return -ENOMEM;
if (mdio_bus_data->irqs)
memcpy(new_bus->irq, mdio_bus_data->irqs, sizeof(new_bus->irq));
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
if (priv->device->of_node)
mdio_bus_data->reset_gpio = -1;
#endif
new_bus->name = "stmmac";
if (priv->plat->has_xgmac) {
new_bus->read = &stmmac_xgmac2_mdio_read;
new_bus->write = &stmmac_xgmac2_mdio_write;
/* Right now only C22 phys are supported */
max_addr = MII_XGMAC_MAX_C22ADDR + 1;
/* Check if DT specified an unsupported phy addr */
if (priv->plat->phy_addr > MII_XGMAC_MAX_C22ADDR)
dev_err(dev, "Unsupported phy_addr (max=%d)\n",
MII_XGMAC_MAX_C22ADDR);
} else {
new_bus->read = &stmmac_mdio_read;
new_bus->write = &stmmac_mdio_write;
max_addr = PHY_MAX_ADDR;
}
new_bus->reset = &stmmac_mdio_reset;
snprintf(new_bus->id, MII_BUS_ID_SIZE, "%s-%x",
new_bus->name, priv->plat->bus_id);
new_bus->priv = ndev;
new_bus->phy_mask = mdio_bus_data->phy_mask;
new_bus->parent = priv->device;
err = of_mdiobus_register(new_bus, mdio_node);
if (err != 0) {
dev_err(dev, "Cannot register the MDIO bus\n");
goto bus_register_fail;
}
stmmac_mdio_write(new_bus,0,31,2627);
stmmac_mdio_write(new_bus,0,25,0x1801);
stmmac_mdio_write(new_bus,0,31,0);
stmmac_mdio_write(new_bus,0,0,0x8000);
if (priv->plat->phy_node || mdio_node)
goto bus_register_done;
found = 0;
for (addr = 0; addr < max_addr; addr++) {
struct phy_device *phydev = mdiobus_get_phy(new_bus, addr);
if (!phydev)
continue;
/*
* If an IRQ was provided to be assigned after
* the bus probe, do it here.
*/
if (!mdio_bus_data->irqs &&
(mdio_bus_data->probed_phy_irq > 0)) {
new_bus->irq[addr] = mdio_bus_data->probed_phy_irq;
phydev->irq = mdio_bus_data->probed_phy_irq;
}
/*
* If we're going to bind the MAC to this PHY bus,
* and no PHY number was provided to the MAC,
* use the one probed here.
*/
if (priv->plat->phy_addr == -1)
priv->plat->phy_addr = addr;
phy_attached_info(phydev);
found = 1;
}
if (!found && !mdio_node) {
dev_warn(dev, "No PHY found\n");
mdiobus_unregister(new_bus);
mdiobus_free(new_bus);
return -ENODEV;
}
bus_register_done:
priv->mii = new_bus;
return 0;2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
stmmac_xgmac2_mdio_read
stmmac_mdio_read
net/phy/mdio_bus.c
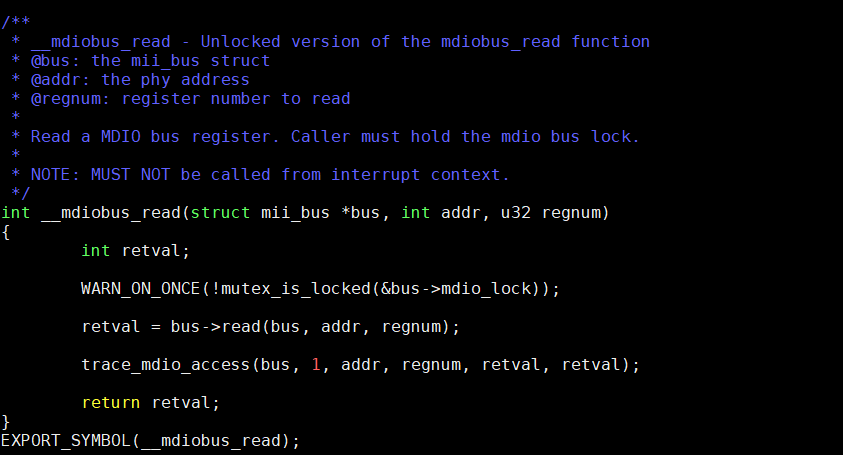
四、注册phy设备
一般动态扫描的phy设备在网卡驱动初始化的时候注册,仍然以stmmac网卡驱动为例,在其平台probe初始化中调用stmmac_dvr_probe函数、最终调用stmmac_mdio_register申请mii_bus后,调用mdiobus_register函数创建并注册phy_device对象。
mdiobus_register(new_bus);