05、MMC子系统数据结构关系
📢本篇章将介绍MMC子系统数据结构关系
一、MMC子系统数据结构
首先我们看几个重要的数据结构:
struct mmc_host:描述设备控制器struct mmc_card:描述设备struct mmc_driver:用来描述MMC设备驱动
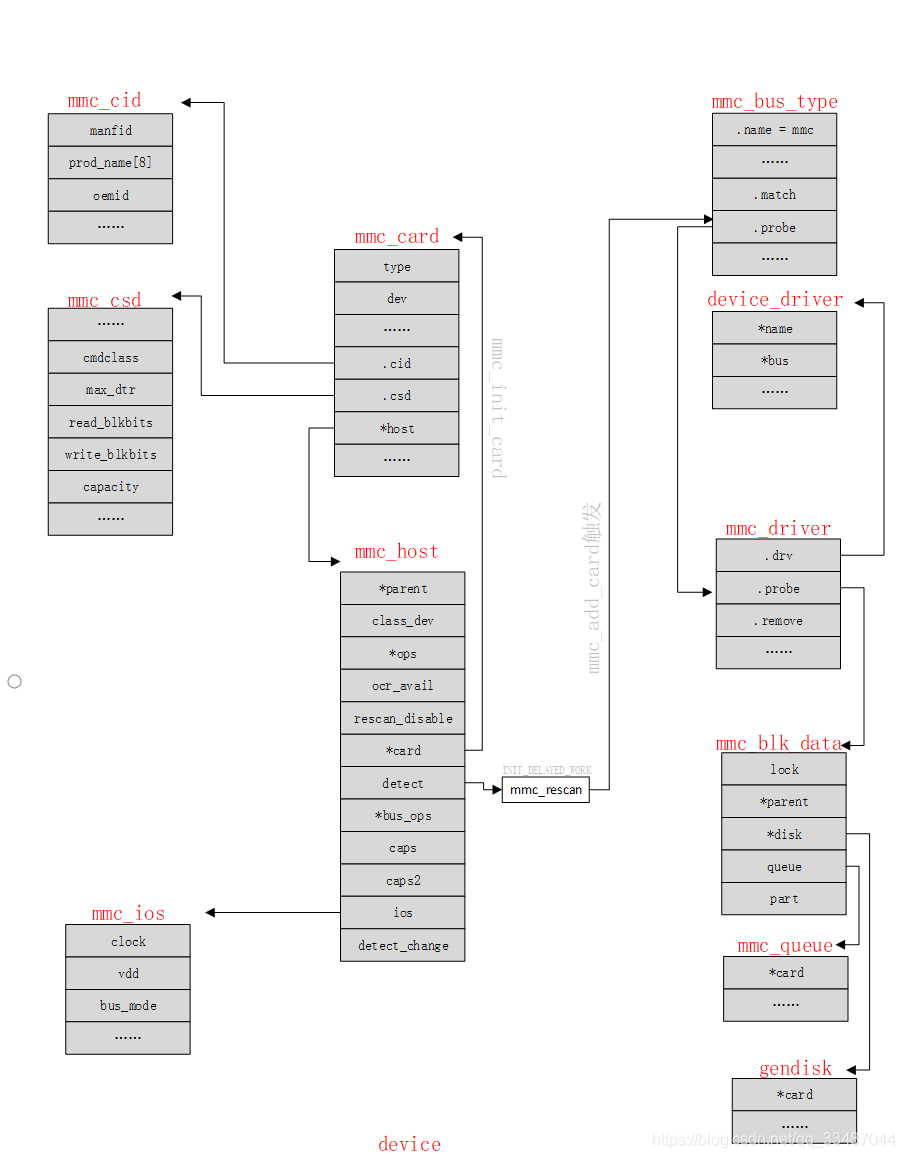
2.1、mmc_host
MMC core使用struct mmc_host结构抽象具体的MMC host controller,该结构的定义位于“include/linux/mmc/host.h”中,它既可以用来描述MMC控制器所具有的特性、能力(host driver关心的内容),也保存了host driver运行过程中的一些状态、参数(MMC core关心的内容)
C++
struct mmc_host {
struct device *parent;
struct device class_dev;
int index;
const struct mmc_host_ops *ops;
struct mmc_pwrseq *pwrseq;
unsigned int f_min;
unsigned int f_max;
unsigned int f_init;
u32 ocr_avail;
u32 ocr_avail_sdio; /* SDIO-specific OCR */
u32 ocr_avail_sd; /* SD-specific OCR */
u32 ocr_avail_mmc; /* MMC-specific OCR */
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
struct notifier_block pm_notify;
#endif
u32 max_current_330;
u32 max_current_300;
u32 max_current_180;
#define MMC_VDD_165_195 0x00000080 /* VDD voltage 1.65 - 1.95 */
#define MMC_VDD_20_21 0x00000100 /* VDD voltage 2.0 ~ 2.1 */
#define MMC_VDD_21_22 0x00000200 /* VDD voltage 2.1 ~ 2.2 */
#define MMC_VDD_22_23 0x00000400 /* VDD voltage 2.2 ~ 2.3 */
#define MMC_VDD_23_24 0x00000800 /* VDD voltage 2.3 ~ 2.4 */
#define MMC_VDD_24_25 0x00001000 /* VDD voltage 2.4 ~ 2.5 */
#define MMC_VDD_25_26 0x00002000 /* VDD voltage 2.5 ~ 2.6 */
#define MMC_VDD_26_27 0x00004000 /* VDD voltage 2.6 ~ 2.7 */
#define MMC_VDD_27_28 0x00008000 /* VDD voltage 2.7 ~ 2.8 */
#define MMC_VDD_28_29 0x00010000 /* VDD voltage 2.8 ~ 2.9 */
#define MMC_VDD_29_30 0x00020000 /* VDD voltage 2.9 ~ 3.0 */
#define MMC_VDD_30_31 0x00040000 /* VDD voltage 3.0 ~ 3.1 */
#define MMC_VDD_31_32 0x00080000 /* VDD voltage 3.1 ~ 3.2 */
#define MMC_VDD_32_33 0x00100000 /* VDD voltage 3.2 ~ 3.3 */
#define MMC_VDD_33_34 0x00200000 /* VDD voltage 3.3 ~ 3.4 */
#define MMC_VDD_34_35 0x00400000 /* VDD voltage 3.4 ~ 3.5 */
#define MMC_VDD_35_36 0x00800000 /* VDD voltage 3.5 ~ 3.6 */
u32 caps; /* Host capabilities */1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
2.2、mmc_card
struct mmc_card是mmc core由mmc设备抽象出来的card设备的结构体,用于代表一个mmc设备。mmc card类型(mmc_card->type)如下:
C
#define MMC_TYPE_MMC 0 /* MMC card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SD 1 /* SD card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SDIO 2 /* SDIO card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SD_COMBO 3 /* SD combo (IO+mem) card */1
2
3
4
2
3
4
card.h
C++
struct mmc_card {
struct mmc_host *host; /* the host this device belongs to */
struct device dev; /* the device */
u32 ocr; /* the current OCR setting */
unsigned int rca; /* relative card address of device */
unsigned int type; /* card type */
#define MMC_TYPE_MMC 0 /* MMC card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SD 1 /* SD card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SDIO 2 /* SDIO card */
#define MMC_TYPE_SD_COMBO 3 /* SD combo (IO+mem) card */
unsigned int state; /* (our) card state */
unsigned int quirks; /* card quirks */
unsigned int quirk_max_rate; /* max rate set by quirks */
#define MMC_QUIRK_LENIENT_FN0 (1<<0) /* allow SDIO FN0 writes outside of the VS CCCR range */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BLKSZ_FOR_BYTE_MODE (1<<1) /* use func->cur_blksize */
/* for byte mode */
#define MMC_QUIRK_NONSTD_SDIO (1<<2) /* non-standard SDIO card attached */
/* (missing CIA registers) */
#define MMC_QUIRK_NONSTD_FUNC_IF (1<<4) /* SDIO card has nonstd function interfaces */
#define MMC_QUIRK_DISABLE_CD (1<<5) /* disconnect CD/DAT[3] resistor */
#define MMC_QUIRK_INAND_CMD38 (1<<6) /* iNAND devices have broken CMD38 */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BLK_NO_CMD23 (1<<7) /* Avoid CMD23 for regular multiblock */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_BYTE_MODE_512 (1<<8) /* Avoid sending 512 bytes in */
/* byte mode */
#define MMC_QUIRK_LONG_READ_TIME (1<<9) /* Data read time > CSD says */
#define MMC_QUIRK_SEC_ERASE_TRIM_BROKEN (1<<10) /* Skip secure for erase/trim */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_IRQ_POLLING (1<<11) /* Polling SDIO_CCCR_INTx could create a fake interrupt */
#define MMC_QUIRK_TRIM_BROKEN (1<<12) /* Skip trim */
#define MMC_QUIRK_BROKEN_HPI (1<<13) /* Disable broken HPI support */
bool reenable_cmdq; /* Re-enable Command Queue */
unsigned int erase_size; /* erase size in sectors */
unsigned int erase_shift; /* if erase unit is power 2 */
unsigned int pref_erase; /* in sectors */
unsigned int eg_boundary; /* don't cross erase-group boundaries */
u8 erased_byte; /* value of erased bytes */
u32 raw_cid[4]; /* raw card CID */
u32 raw_csd[4]; /* raw card CSD */
u32 raw_scr[2]; /* raw card SCR */
u32 raw_ssr[16]; /* raw card SSR */
struct mmc_cid cid; /* card identification */
struct mmc_csd csd; /* card specific */
struct mmc_ext_csd ext_csd; /* mmc v4 extended card specific */
struct sd_scr scr; /* extra SD information */
struct sd_ssr ssr; /* yet more SD information */
struct sd_switch_caps sw_caps; /* switch (CMD6) caps */
unsigned int sdio_funcs; /* number of SDIO functions */
struct sdio_cccr cccr; /* common card info */
struct sdio_cis cis; /* common tuple info */
struct sdio_func *sdio_func[SDIO_MAX_FUNCS]; /* SDIO functions (devices) */
struct sdio_func *sdio_single_irq; /* SDIO function when only one IRQ active */
unsigned num_info; /* number of info strings */
const char **info; /* info strings */
struct sdio_func_tuple *tuples; /* unknown common tuples */
unsigned int sd_bus_speed; /* Bus Speed Mode set for the card */
unsigned int mmc_avail_type; /* supported device type by both host and card */
unsigned int drive_strength; /* for UHS-I, HS200 or HS400 */
struct dentry *debugfs_root;
struct mmc_part part[MMC_NUM_PHY_PARTITION]; /* physical partitions */
unsigned int nr_parts;
unsigned int bouncesz; /* Bounce buffer size */
struct workqueue_struct *complete_wq; /* Private workqueue */
};1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
2.3、mmc_host_ops
struct mmc_host_ops抽象并集合了MMC host controller所有的操作函数集
host.h
C++
struct mmc_host_ops {
/*
* It is optional for the host to implement pre_req and post_req in
* order to support double buffering of requests (prepare one
* request while another request is active).
* pre_req() must always be followed by a post_req().
* To undo a call made to pre_req(), call post_req() with
* a nonzero err condition.
*/
void (*post_req)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req,
int err);
void (*pre_req)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
void (*request)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
/*
* Avoid calling the next three functions too often or in a "fast
* path", since underlaying controller might implement them in an
* expensive and/or slow way. Also note that these functions might
* sleep, so don't call them in the atomic contexts!
*/
/*
* Notes to the set_ios callback:
* ios->clock might be 0. For some controllers, setting 0Hz
* as any other frequency works. However, some controllers
* explicitly need to disable the clock. Otherwise e.g. voltage
* switching might fail because the SDCLK is not really quiet.
*/
void (*set_ios)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
/*
* Return values for the get_ro callback should be:
* 0 for a read/write card
* 1 for a read-only card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*/
int (*get_ro)(struct mmc_host *host);
/*
* Return values for the get_cd callback should be:
* 0 for a absent card
* 1 for a present card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*/
int (*get_cd)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*enable_sdio_irq)(struct mmc_host *host, int enable);
void (*ack_sdio_irq)(struct mmc_host *host);
/* optional callback for HC quirks */
void (*init_card)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
int (*start_signal_voltage_switch)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
/* Check if the card is pulling dat[0:3] low */
int (*card_busy)(struct mmc_host *host);
int (*set_sdio_status)(struct mmc_host *host, int val);
/* The tuning command opcode value is different for SD and eMMC cards */
int (*execute_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, u32 opcode);
/* Prepare HS400 target operating frequency depending host driver */
int (*prepare_hs400_tuning)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
/* Prepare for switching from HS400 to HS200 */
void (*hs400_downgrade)(struct mmc_host *host);1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
2.4、mmc_pwrseq
MMC框架的供电控制功能有一个很实用的设计。它通过一个叫struct mmc_pwrseq_ops的函数集合,集中管理了设备上电、断电等操作。这些函数专门用来控制存储卡(如SD卡或eMMC)的电源开关。
在系统核心部分(drivers/mmc/core/pwrseq.c),MMC框架提供了一个通用的供电管理工具。同时,还内置了几种现成的供电策略实现,比如简单的通用方案(pwrseq_simple.c)和专门针对eMMC的优化方案(pwrseq_emmc.c)。这样设计的最终目标是:开发者只需要在设备树(DTS)配置文件里做简单设置,就能自动适配对应的供电控制逻辑,无需复杂的手动编程。
core/pwrseq.h
C++
struct mmc_pwrseq_ops {
void (*pre_power_on)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*post_power_on)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*power_off)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*reset)(struct mmc_host *host);
};
struct mmc_pwrseq {
const struct mmc_pwrseq_ops *ops;
struct device *dev;
struct list_head pwrseq_node;
struct module *owner;
};1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14